The gynecological system refers to the reproductive system in females, encompassing the organs and structures involved in reproduction, menstruation, and hormonal regulation. Key components of the gynecological system include the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina. Additionally, the breasts are often considered part of the gynecological system due to their involvement in lactation and hormonal regulation.
Disorders affecting the gynecological system can have a significant impact on women’s health and quality of life, leading to symptoms such as pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, infertility, and reproductive complications. These disorders can arise from various factors, including hormonal imbalances, infections, structural abnormalities, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle factors.
One common gynecological disorder is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal condition characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, ovarian cysts, and elevated androgen levels. PCOS can lead to symptoms such as hirsutism (excessive hair growth), acne, weight gain, and infertility. Management of PCOS typically involves lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and exercise, along with medications to regulate menstrual cycles and address symptoms such as acne and hirsutism.
Endometriosis is another prevalent gynecological disorder characterized by the presence of endometrial-like tissue outside the uterus, commonly in the pelvic cavity. Endometriosis can cause symptoms such as pelvic pain, painful menstruation (dysmenorrhea), and infertility. Treatment options for endometriosis may include pain management, hormonal therapy, surgical interventions to remove endometrial implants or adhesions, and assisted reproductive technologies for women struggling with infertility.
Uterine fibroids, or leiomyomas, are benign tumors that develop within the muscular wall of the uterus. Fibroids can lead to symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pressure, urinary frequency, and reproductive difficulties. Treatment for uterine fibroids may include medications to manage symptoms, minimally invasive procedures such as uterine artery embolization or focused ultrasound surgery, and surgical interventions such as myomectomy or hysterectomy, depending on the size, location, and symptoms associated with the fibroids.
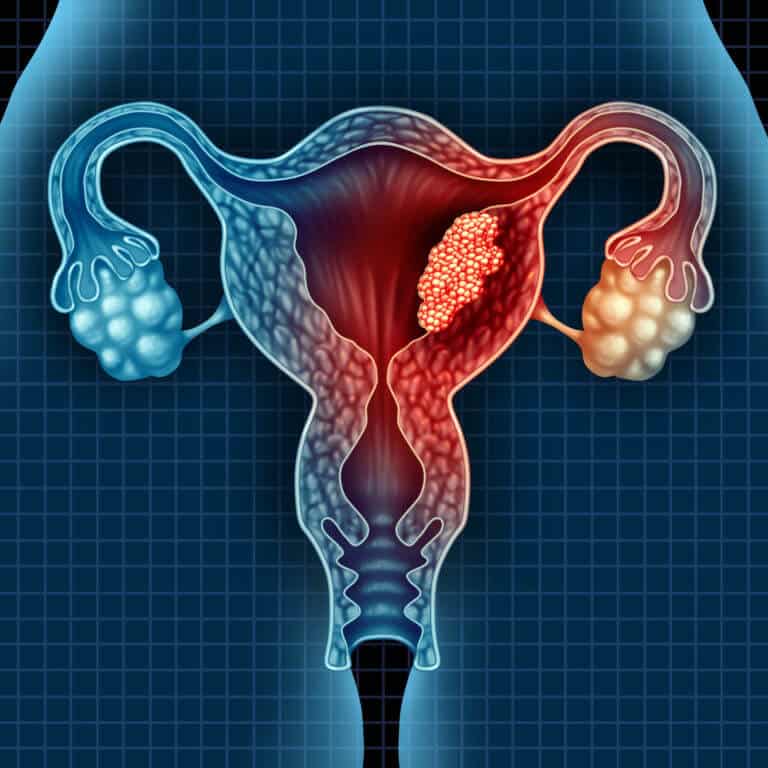
Gynecological cancers, including cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, and vaginal cancer, represent significant health concerns and can have serious consequences if not detected and treated early. Screening tests such as Pap smears, HPV testing, and transvaginal ultrasound can help detect gynecological cancers at an early stage when treatment is most effective. Treatment options for gynecological cancers may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy, depending on the type and stage of cancer.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are another important aspect of gynecological health, affecting millions of women worldwide each year. STIs such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and human papillomavirus (HPV) can lead to a range of complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and certain gynecological cancers. Prevention strategies for STIs include safer sex practices, regular STI testing, vaccination against HPV, and prompt treatment of infections.
Overall, maintaining gynecological health requires regular preventive care, including routine pelvic examinations, Pap smears, and screenings for STIs, along with timely medical evaluation and management of any gynecological symptoms or concerns. By promoting awareness, education, and access to comprehensive gynecological care, it is possible to improve women’s health outcomes and enhance their overall well-being across the lifespan.